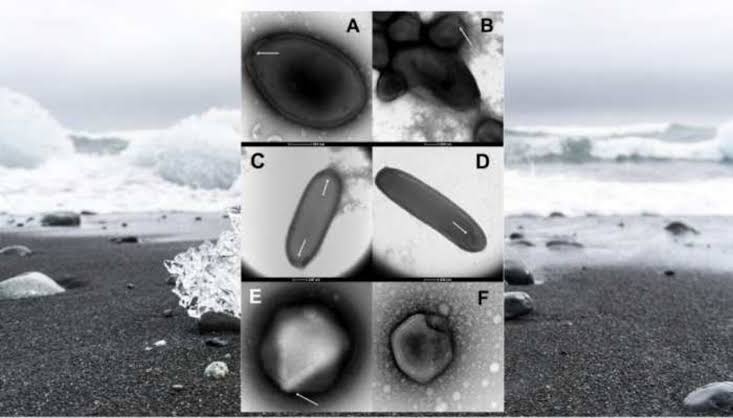
London: European researchers examined ancient samples collected from permafrost in the Siberia region of Russia including one frozen under a lake more than 48,500 years ago. They revived and characterized 13 new pathogens, what they termed “zombie viruses,” and found that they remained infectious despite spending many millennia trapped in the frozen ground.
Scientists have long warned that the thawing of permafrost due to atmospheric warming will worsen climate change by freeing previously trapped greenhouse gases like methane. But its effect on dormant pathogens is less well understood.
The team of researchers from Russia, Germany, and France said the biological risk of reanimating the viruses they studied was “totally negligible” due to the strains they targeted, mainly those capable of infecting amoeba microbes. The potential revival of a virus that could infect animals or humans is much more problematic, they said, warning that their work can be extrapolated to show the danger is real.
“It is thus likely that ancient permafrost will release these unknown viruses upon thawing,” they wrote in an article posted to the preprint repository bioRxiv that hasn’t yet been peer-reviewed. “How long these viruses could remain infectious once exposed to outdoor conditions, and how likely they will be to encounter and infect a suitable host in the interval, is yet impossible to estimate.”
“But the risk is bound to increase in the context of global warming when permafrost thawing will keep accelerating, and more people will be populating the Arctic in the wake of industrial ventures,” they said.