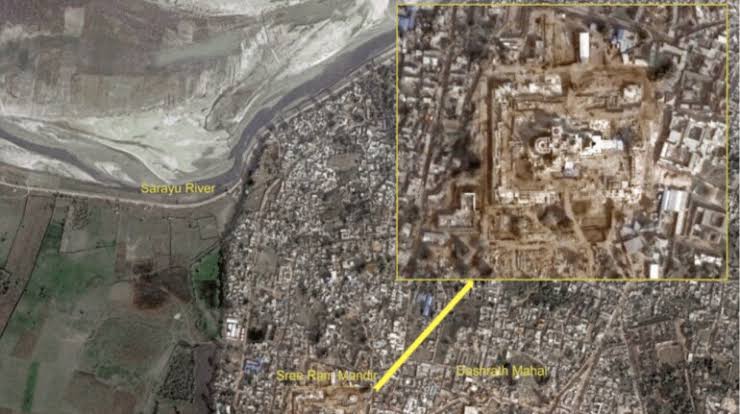
New Delhi: The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has captured satellite images of Ayodhya’s Ram Mandir. In these images, captured by the Indian Remote Sensing Satellite, one can see the Dashrath Mahal, the Sarayu River, and the recently renovated Ayodhya railway station.
The temple will be consecrated on January 22. Ayodhya has been decorated, and murals and paintings made. Sun pillars, on which ‘Jai Shree Ram’ has been inscribed, have been established.
Walls have been built along the Dharma Path to depict events from Ramayan stories, and they have been adorned with intricately crafted terracotta murals. Other features, such as CCTV surveillance and smart traffic systems, have been installed.
The temple has been built in the traditional Nagara style and has a length (east-west) of 380 feet, a width of 250 feet, and a height of 161 feet. Nagara architecture is a style of temple architecture that originated in North India.
The temple has tall pyramidal towers called Shikharas. Each has a Kalash at the top. The pillars of the temples are carved with intricate designs, and the walls are decorated with sculptures and reliefs.
The temple complex is divided into six parts, including the sanctum sanctorum and five pavilions—Gun Mandap, Rang Mandap, Nritya Mandap, Kirtan Mandap, Prarthana Mandap.
A designated parikrama path encircles the temple. This is a walkway traditionally used by devotees to perform circumambulation, a ritual practice signifying reverence and respect.


Comments are closed.